- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊# 前言
上周学习了inceptionv1网络,这周学习其改进版本inceptionv3
简介
Inception v3是谷歌研究团队提出的深度卷积神经网络架构,通过引入多尺度的Inception模块和辅助分类器等技术,有效解决了深度网络训练中的梯度消失和模型参数过多的问题。该网络利用不同大小的卷积核并行处理图像信息,结合Batch Normalization和全局平均池化等优化策略,以较少的参数实现了优异的图像分类和识别性能,成为了深度学习图像处理领域的重要里程碑之一。下面分别进行介绍
网络结构特点
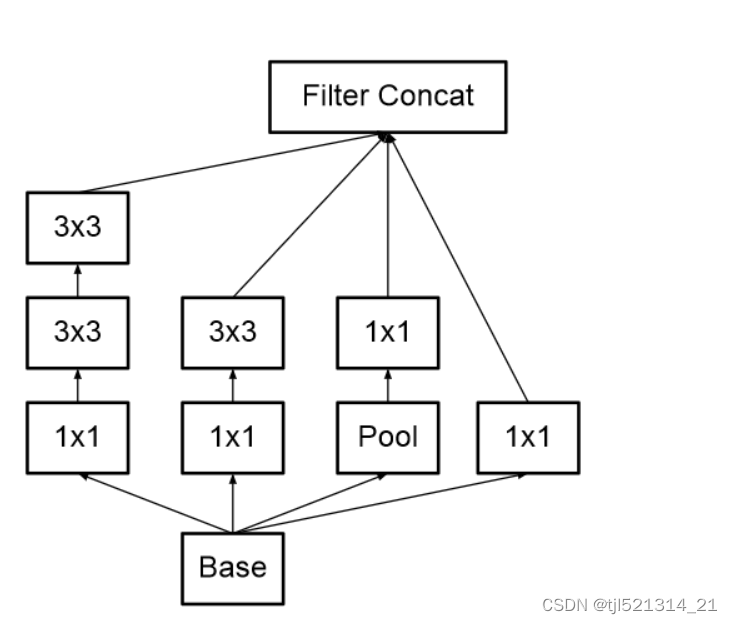
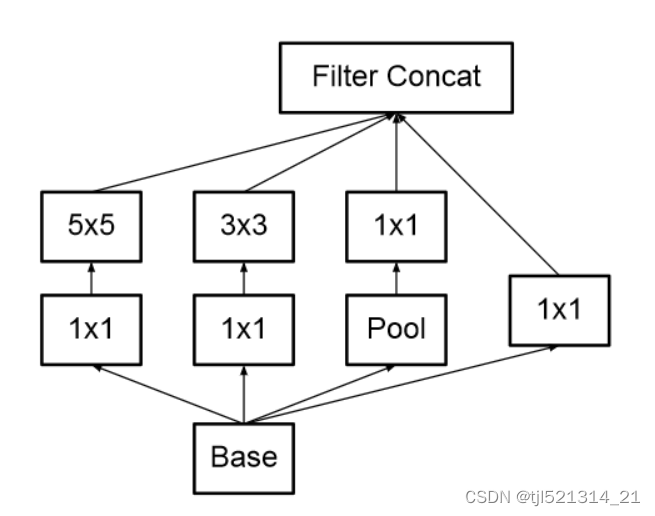
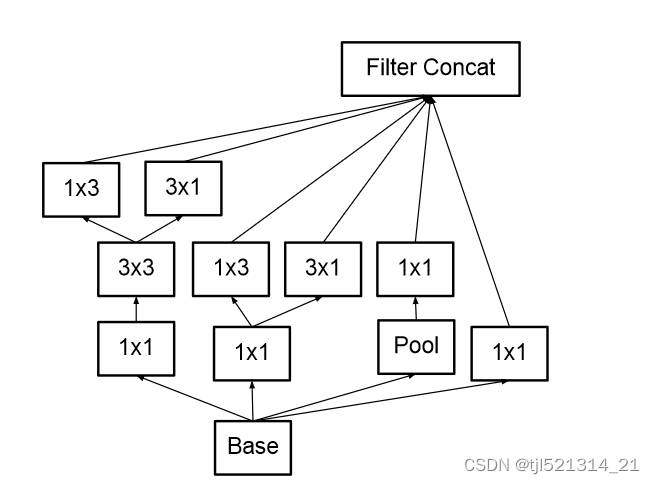
1.用5x5卷积代替3x3卷积,如下图所示
2.将nxn卷积分解
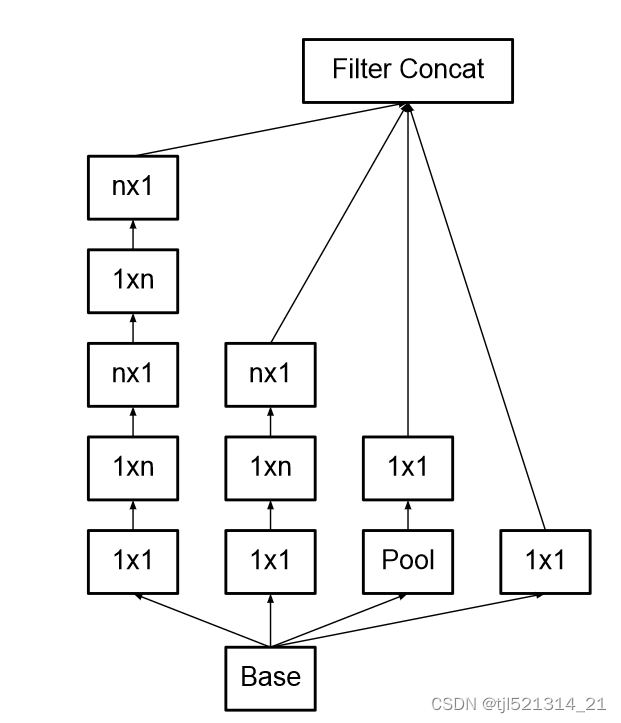
如将3x3卷积分解为1x3和3x1,为了减少参数量和计算量
代码实现
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
from torchsummary import summary
class GoogLeNetV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNetV3, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
# 3个3×3卷积替代7×7卷积
self.conv1_1 = BasicConv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
self.conv1_2 = BasicConv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
self.conv1_3 = BasicConv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# 池化层
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 80, kernel_size=3)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(80, 192, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
self.conv4 = BasicConv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.inception3a = InceptionV3A(192, 64, 48, 64, 64, 96, 32)
self.inception3b = InceptionV3A(256, 64, 48, 64, 64, 96, 64)
self.inception3c = InceptionV3A(288, 64, 48, 64, 64, 96, 64)
self.inception4a = InceptionV3D(288, 0, 384, 384, 64, 96, 0)
self.inception4b = InceptionV3B(768, 192, 128, 192, 128, 192, 192)
self.inception4c = InceptionV3B(768, 192, 160, 192, 160, 192, 192)
self.inception4d = InceptionV3B(768, 192, 160, 192, 160, 192, 192)
self.inception4e = InceptionV3D(768, 0, 384, 384, 64, 128, 0)
if self.aux_logits == True:
self.aux = InceptionAux(in_channels=768, out_channels=num_classes)
self.inception5a = InceptionV3C(1280, 320, 384, 384, 448, 384, 192)
self.inception5b = InceptionV3C(2048, 320, 384, 384, 448, 384, 192)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc = nn.Linear(2048, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 299 x 299
x = self.conv1_1(x)
# N x 32 x 149 x 149
x = self.conv1_2(x)
# N x 32 x 147 x 147
x = self.conv1_3(x)
# N x 32 x 147 x 147
x = self.maxpool1(x)
# N x 64 x 73 x 73
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 80 x 71 x 71
x = self.conv3(x)
# N x 192 x 35 x 35
x = self.conv4(x)
# N x 192 x 35 x 35
x = self.inception3a(x)
# N x 256 x 35 x 35
x = self.inception3b(x)
# N x 288 x 35 x 35
x = self.inception3c(x)
# N x 288 x 35x 35
x = self.inception4a(x)
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
x = self.inception4b(x)
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
x = self.inception4c(x)
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
x = self.inception4d(x)
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux = self.aux(x)
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
x = self.inception4e(x)
# N x 1280 x 8 x 8
x = self.inception5a(x)
# N x 2048 x 8 x 8
x = self.inception5b(x)
# N x 2048 x 7 x 7
x = self.avgpool(x)
# N x 2048 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
# N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# N x 1000(num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # 训练阶段使用
return x, aux
return x
# 对模型的权重进行初始化操作
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# InceptionV3A:BasicConv2d+MaxPool2d
class InceptionV3A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, pool_proj):
super(InceptionV3A, self).__init__()
# 1×1卷积
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
# 1×1卷积+3×3卷积
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 1×1卷积++3×3卷积+3×3卷积
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3redX2, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 3×3池化+1×1卷积
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
# 拼接
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# InceptionV3B:BasicConv2d+MaxPool2d
class InceptionV3B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, pool_proj):
super(InceptionV3B, self).__init__()
# 1×1卷积
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
# 1×1卷积+1×3卷积+3×1卷积
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=[1, 3], padding=[0, 1]),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3, ch3x3, kernel_size=[3, 1], padding=[1, 0]) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 1×1卷积+1×3卷积+3×1卷积+1×3卷积+3×1卷积
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3redX2, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[1, 3], padding=[0, 1]),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[3, 1], padding=[1, 0]),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[1, 3], padding=[0, 1]),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[3, 1], padding=[1, 0]) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
# 3×3池化+1×1卷积
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
# 拼接
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# InceptionV3C:BasicConv2d+MaxPool2d
class InceptionV3C(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, pool_proj):
super(InceptionV3C, self).__init__()
# 1×1卷积
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
# 1×1卷积+1×3卷积+3×1卷积
self.branch2_0 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2_1 = BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=[1, 3], padding=[0, 1])
self.branch2_2 = BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=[3, 1], padding=[1, 0])
# 1×1卷积+3×3卷积+1×3卷积+3×1卷积
self.branch3_0 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3redX2, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
)
self.branch3_1 = BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[1, 3], padding=[0, 1])
self.branch3_2 = BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=[3, 1], padding=[1, 0])
# 3×3池化+1×1卷积
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2_0 = self.branch2_0(x)
branch2 = torch.cat([self.branch2_1(branch2_0), self.branch2_2(branch2_0)], dim=1)
branch3_0 = self.branch3_0(x)
branch3 = torch.cat([self.branch3_1(branch3_0), self.branch3_2(branch3_0)], dim=1)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
# 拼接
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# InceptionV3D:BasicConv2d+MaxPool2d
class InceptionV3D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, pool_proj):
super(InceptionV3D, self).__init__()
# ch1x1:没有1×1卷积
# 1×1卷积+3×3卷积,步长为2
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 1×1卷积+3×3卷积+3×3卷积,步长为2
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3redX2, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3redX2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
BasicConv2d(ch3x3X2, ch3x3X2, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
)
# 3×3池化,步长为2
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2))
# pool_proj:池化层后不再接卷积层
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
# 拼接
outputs = [branch1,branch2, branch3]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# 辅助分类器:AvgPool2d+BasicConv2d+Linear+dropout
class InceptionAux(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=768, kernel_size=5, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.7)
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features=768, out_features=out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
# N x 768 x 17 x 17
x = self.averagePool(x)
# N x 768 x 5 x 5
x = self.conv1(x)
# N x 128 x 5 x 5
x = self.conv2(x)
# N x 768 x 1 x 1
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
# N x 768
out = self.linear(self.dropout(x))
# N x num_classes
return out
# 卷积组: Conv2d+BN+ReLU
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# model = GoogLeNetV3().to(device)
# summary(model, input_size=(3, 299, 299))
model = GoogLeNetV3(num_classes=4).to(device)
summary(model, input_size=( 3, 299, 299))
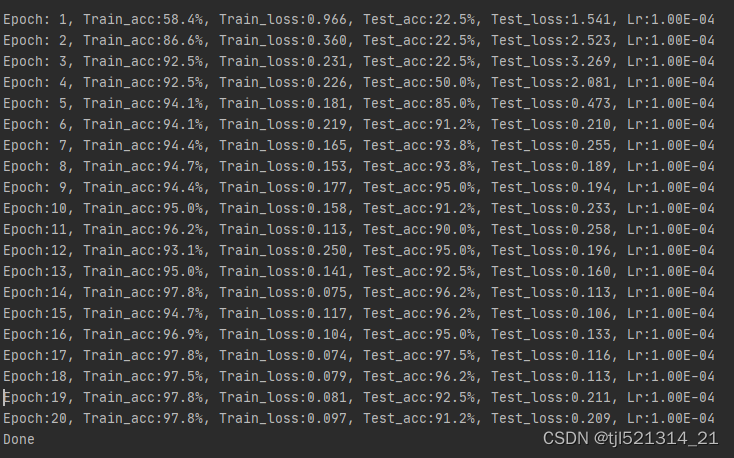
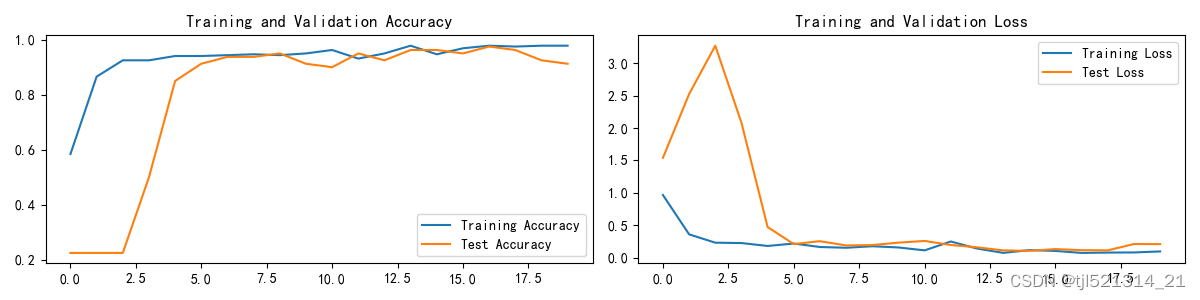
模型验证
使用天气分类数据集
总结
Inception v3使用不同大小的卷积核并行处理输入,允许网络同时学习局部和全局特征,提高了特征提取的效率和准确性。通过把大的卷积核分解为小卷积核可减少参数量。Inception模型中广泛使用了多尺度卷积,通过并行使用不同大小的卷积核,有效地提高了模型对图像特征的提取效率和准确性。